On a quiet night in 1957, something very unusual happened. A new “star” appeared in the sky, but it was not a star at all. It was a small, metal ball, and it was sending out a simple “beep… beep… beep…” radio signal. That sound, which was picked up by radios all over the world, was a huge moment for humanity. It was the moment that the Space Age began, and it was the moment that the world changed forever.
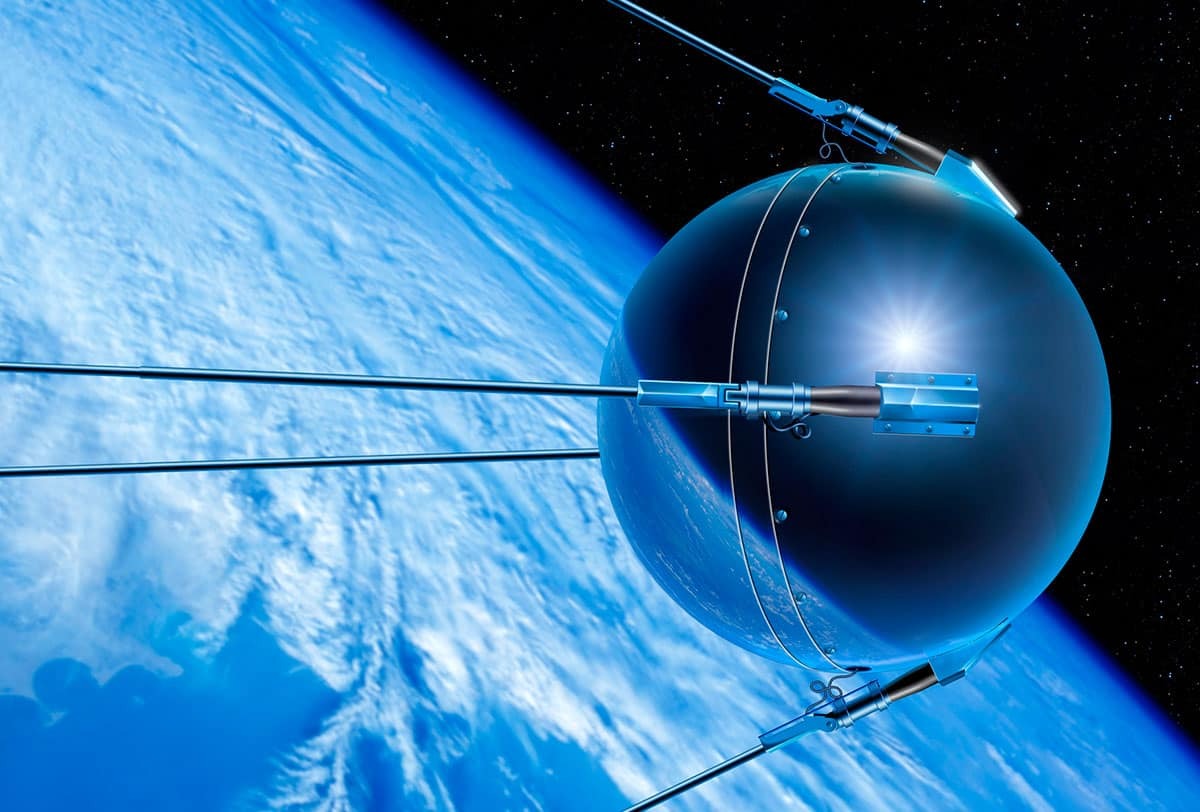
The beeping ball was called Sputnik 1, and it was the world’s first artificial satellite. Its launch by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957, was a huge shock to the world. It showed that it was possible to launch a man-made object into orbit around the Earth. But more importantly, it started a fierce competition between two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, that would change the course of history: the Space Race.
In this article, we will take a deep dive into the story of Sputnik’s launch, its context in the Cold War, and its immense impact on the world, from the start of the Space Race to the creation of NASA.
The World in 1957: A Time of Cold War
To understand the impact of Sputnik, you have to understand the time in which it was launched. The world was in the middle of the Cold War, a tense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union. The two nations were locked in a competition for military power, political influence, and technological superiority.
The Soviet Union and the United States both had nuclear weapons, and they were both working on powerful rockets that could carry those weapons across the world. The rockets that could launch a satellite into space were very similar to the rockets that could carry a nuclear bomb. So, when the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, it was not just a scientific victory; it was a military and political one. It showed the world that the Soviets had the technology to launch a rocket into space, and that they might also have a rocket that could carry a nuclear bomb to the U.S.
What Was Sputnik? A Simple, Beeping Satellite
Sputnik 1 was not a very complex machine. It was a polished metal ball, about 23 inches (58 centimeters) wide, with four long antennas. It weighed about 184 pounds (83 kilograms). Its main job was to send out a simple “beep… beep… beep…” radio signal that could be heard by anyone with a radio. It had a few small batteries inside that powered its radio signals.
The satellite did not have any cameras or fancy scientific tools. Its purpose was to prove that it could be done. Its beeping signal was a powerful message to the world that the Soviet Union had been successful. The satellite orbited the Earth for about three weeks before its batteries ran out, and it burned up in the atmosphere a few months later. But its impact was much bigger than its size or its short life.
The Shock of Sputnik: A Wake-Up Call for America
The launch of Sputnik was a huge shock to the United States. It was a surprise because many Americans had thought that their country was far ahead of the Soviet Union in technology. The Soviet Union’s success made many Americans feel like they were falling behind. It was a huge blow to the nation’s pride and a source of fear.
This shock led to a huge amount of public and political pressure on the U.S. government to do something to catch up. People were worried that if the Soviets were ahead in space, they might also be ahead in military technology. This fear and the call to action would lead to some of the most important changes in American history.
The Early Soviet Victories: More “Firsts” in Space
The launch of Sputnik 1 was just the beginning of a series of early victories for the Soviet Union in the Space Race.
- Sputnik 2 and Laika: Just one month after Sputnik 1, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 2. This satellite was bigger, and it carried the first living creature into orbit, a dog named Laika. This was a major step forward, as it showed that a living being could survive in space. Sadly, the technology to bring a living being back to Earth had not yet been developed, and Laika died in space.
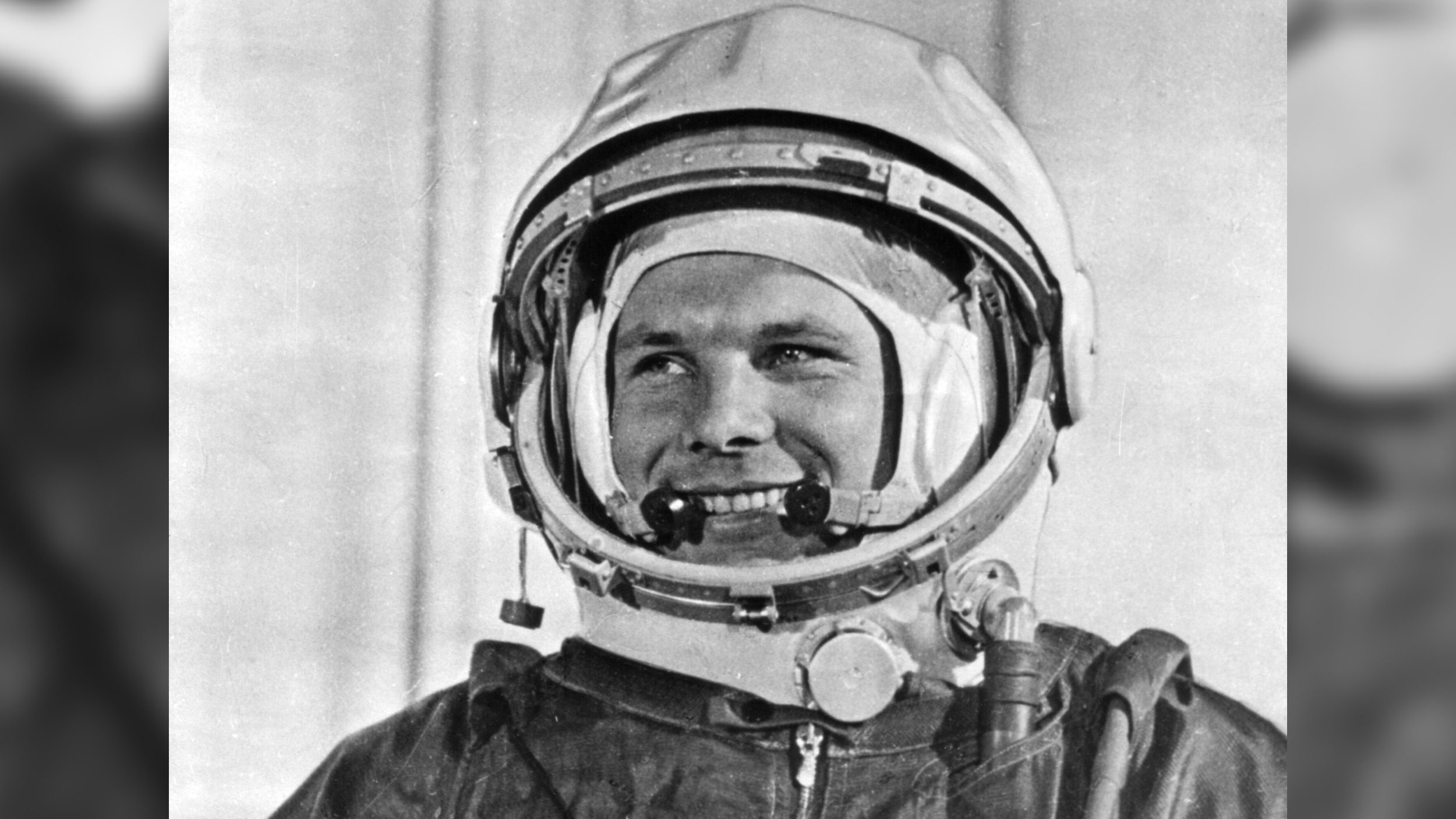
- Yuri Gagarin: On April 12, 1961, the Soviet Union had its biggest triumph yet. A young Soviet pilot named Yuri Gagarin became the first human to travel into space. He orbited the Earth for about 108 minutes and returned safely. His journey was a huge victory for the Soviet Union, and it made him a global hero. His flight proved that humans could survive in space, and it put a huge amount of pressure on the U.S. to do something even bigger.
The American Response: A New Era of Science
The Soviet Union’s early successes were a huge wake-up call for the United States. The U.S. government knew that it had to act fast to catch up. The response was a huge national effort that would change the country forever.
- Creation of NASA: The U.S. government created a new civilian agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), to lead the space program. NASA was created in 1958 with the goal of being a leader in space science and exploration.
- Investment in Education: The U.S. government also realized that it needed to create a new generation of scientists and engineers. It passed a law that provided a huge amount of money for science and math education in schools. This investment would lead to a new generation of scientists and engineers who would eventually win the Space Race.
- Project Mercury and Gemini: NASA started two new space programs, Project Mercury and Project Gemini, as stepping stones to the Moon. Project Mercury was designed to send the first American into space, and Project Gemini was designed to teach astronauts how to live in space for a long time and to practice skills that they would need for the Moon mission.
The Legacy of Sputnik: A New Chapter for Humanity
The launch of Sputnik had a huge and long-lasting impact on the world.
- The Start of the Space Age: The launch of Sputnik was the moment that the Space Age began. It showed the world that space was a place that could be reached, and it opened up a new frontier for humanity to explore.
- Technological Advances: The competition between the two superpowers led to a huge number of technological advances that we still benefit from today. The need for lightweight and powerful technology in space led to the development of microchips and computer technology.
- A New View of Earth: The satellites that were launched in the early days of the Space Race gave us a new view of Earth. They gave us our first pictures of Earth from space, which showed us that our planet is a small, fragile, and beautiful place.
- A New Era of Cooperation: While the Space Race started as a competition, it eventually led to a new era of cooperation. The U.S. and the Soviet Union learned to work together in space, and this cooperation led to the creation of the International Space Station, a symbol of international partnership.
Conclusion
The launch of Sputnik 1, a small, beeping satellite, was a monumental moment in human history. It was a wake-up call that started the Space Race and pushed two superpowers to compete for the cosmos. The rivalry led to a huge amount of technological advances and some of the most famous moments in history, including the first human in space and the first human on the Moon.